History

Greek history can be traced all the way back to Stone Age Hunters and early farmers. It begins at about 8,000BCE (Mesolithic Period) to 30BCE (Cleopatra's death-end of Ancient Greece period).
A Background
The Minoan and Mycenaean civilizations are considered to be the founders of Ancient Greece. The Minoans occupied an island off mainland Greece called Crete. They were sea fairing peoples and did much trade with the Mycenaean's. The Mycenaean's came from the grasslands of southern Russia. As well as trade, they also learned a great deal from the Minoans. The Mycenaean's began the Trojan War because Troy was unfairly taxing the trade ships of the Mycenaean's. This war is famous for the Trojan Horse; hidden inside were the best of the Mycenaean soldiers. The Trojan's took the horse for a peace offering and took it into the city, but that night, the soldiers inside unlocked the gates to Troy and the rest of the army entered and defeated the Trojans.
After the war, the Mycenaean's never settled back to being peaceful. so, in the aftermath of the war, was the Dark Ages.
A Timeline
· 7000BCE-trade in food(eg. Markets), simple huts, fishing
· 2000BCE-destruction of Minoan settlements
· 1400BCE-Mycenaean trade expanding
· 1370BCE- Kronoss' Palace destroyed
· 1250BCE-Trojan War
· 1000BCE-end Mycenaean civilisation
· 776BCE-first Olympic games
· 750BCE-invention of Greek alphabet
· 594BCE-Solon lays foundation for democracy in Athens. Introduces Athens to first coinage and a system of weights and measures
· 510BCE-introduction of democracy in Athens
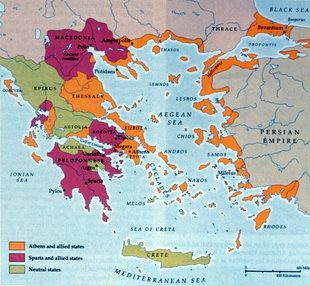
· 500-336BCE-Greece is divided into small city states
· 449BCE-Acropolis and other major building projects begin in Athens
· 447BCE-Parthenon begins construction
· 420BCE-construction of the temple Athena Nike
· 336BCE-Alexander the Great become king of Macedonia
· 329BCE-Alexander’s army reach Bactria (Afghanistan)
· 326BCE-Alexander’s army reach India
· 323BCE-Death of Alexander the Great
· 146BCE-Rome invades Greece. Greece ruled by Rome
· 30BCE-death of Cleopatra. End ‘Ancient Greece’ period
A Background
The Minoan and Mycenaean civilizations are considered to be the founders of Ancient Greece. The Minoans occupied an island off mainland Greece called Crete. They were sea fairing peoples and did much trade with the Mycenaean's. The Mycenaean's came from the grasslands of southern Russia. As well as trade, they also learned a great deal from the Minoans. The Mycenaean's began the Trojan War because Troy was unfairly taxing the trade ships of the Mycenaean's. This war is famous for the Trojan Horse; hidden inside were the best of the Mycenaean soldiers. The Trojan's took the horse for a peace offering and took it into the city, but that night, the soldiers inside unlocked the gates to Troy and the rest of the army entered and defeated the Trojans.
After the war, the Mycenaean's never settled back to being peaceful. so, in the aftermath of the war, was the Dark Ages.
A Timeline
· 7000BCE-trade in food(eg. Markets), simple huts, fishing
· 2000BCE-destruction of Minoan settlements
· 1400BCE-Mycenaean trade expanding
· 1370BCE- Kronoss' Palace destroyed
· 1250BCE-Trojan War
· 1000BCE-end Mycenaean civilisation
· 776BCE-first Olympic games
· 750BCE-invention of Greek alphabet
· 594BCE-Solon lays foundation for democracy in Athens. Introduces Athens to first coinage and a system of weights and measures
· 510BCE-introduction of democracy in Athens
· 500-336BCE-Greece is divided into small city states
· 449BCE-Acropolis and other major building projects begin in Athens
· 447BCE-Parthenon begins construction
· 420BCE-construction of the temple Athena Nike
· 336BCE-Alexander the Great become king of Macedonia
· 329BCE-Alexander’s army reach Bactria (Afghanistan)
· 326BCE-Alexander’s army reach India
· 323BCE-Death of Alexander the Great
· 146BCE-Rome invades Greece. Greece ruled by Rome
· 30BCE-death of Cleopatra. End ‘Ancient Greece’ period
Geography
Greece is located in south-eastern Europe. It can be easily divided into three section: Northern Greece, Central Greece and the Peloponnese. Greece stretches from the Balkans into the Mediterranean Sea. Along with it's many gulfs and bays, the area is generally quite mountainous with the exception of some forests.
Greece has 1,200 to 6,000 islands, depending on the minimum size. These islands include: Santorini, Crete, Hydra and thousands of others.
Greece's lands are mostly stony and only suitable for grazing. However, other areas of Greece are better suited to growing crops like wheat, barely, citrus, dates and olives.
Greece has 1,200 to 6,000 islands, depending on the minimum size. These islands include: Santorini, Crete, Hydra and thousands of others.
Greece's lands are mostly stony and only suitable for grazing. However, other areas of Greece are better suited to growing crops like wheat, barely, citrus, dates and olives.
Famous Landmarks
Many landmarks in Greece are ancient buildings, temples and places of great religious significance. These places include:·
- Acropolis- a building containing the remains of several ancient buildings
- Temple Athena Nike- 'Nike' means victory. This is a temple dedicated to Athena.
- Parthenon- a temple dedicated to the Goddess Athena; the patron of Athens
- Mt. Olympus- the birth place of the Gods and Goddesses
- Olympia- where the Olympics were held
- Athens- capital of Greece, ancient and modern
- Sparta- a city state unlike all others
- Delphi- the Oracle of Delphi. Located in the ancient temple of Apollo